IVY CHEN, MPH
Lecturer, ivychen@berkeley.edu
IB 140: Human
Sexuality & Reproduction
Diagrams: Sperm, Semen & Spermatogenesis
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
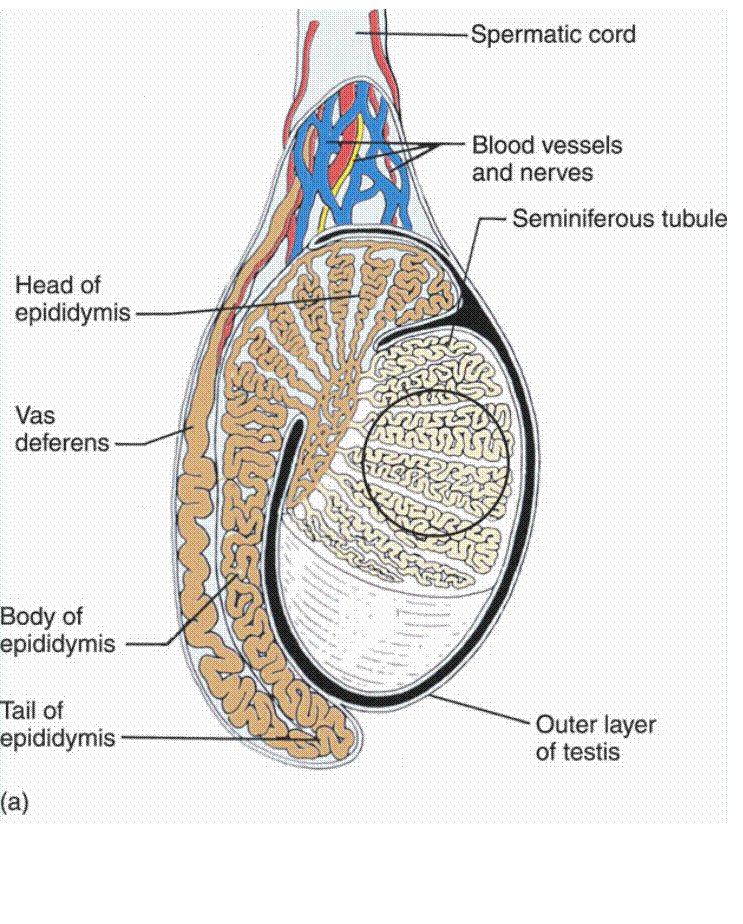
Cross section of seminiferous
tubule
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
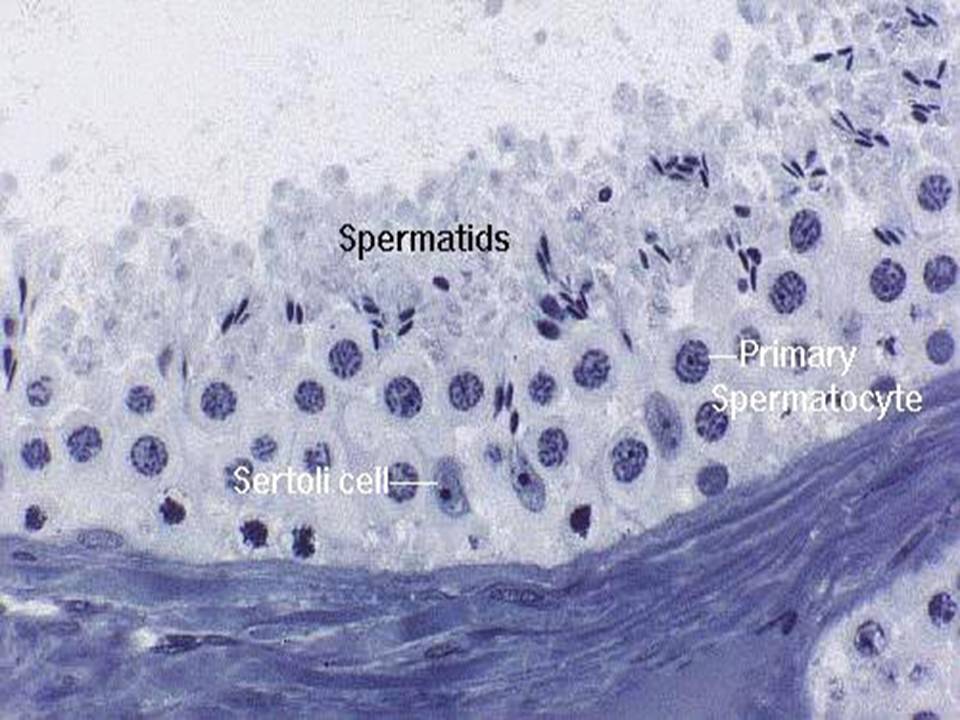
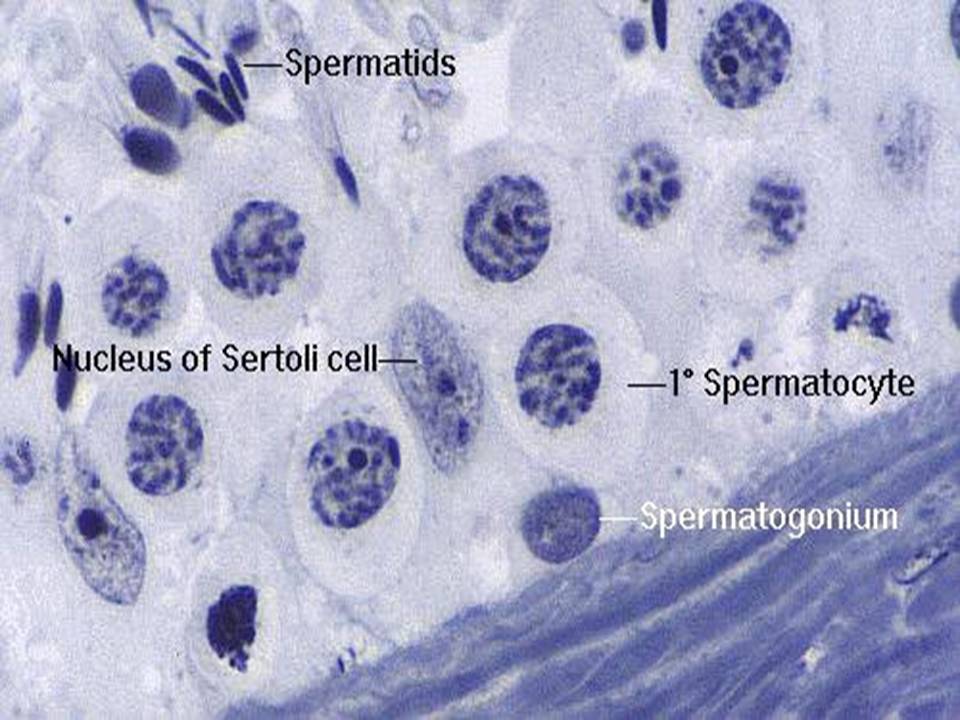
Close-up
histological slides of seminiferous tubule
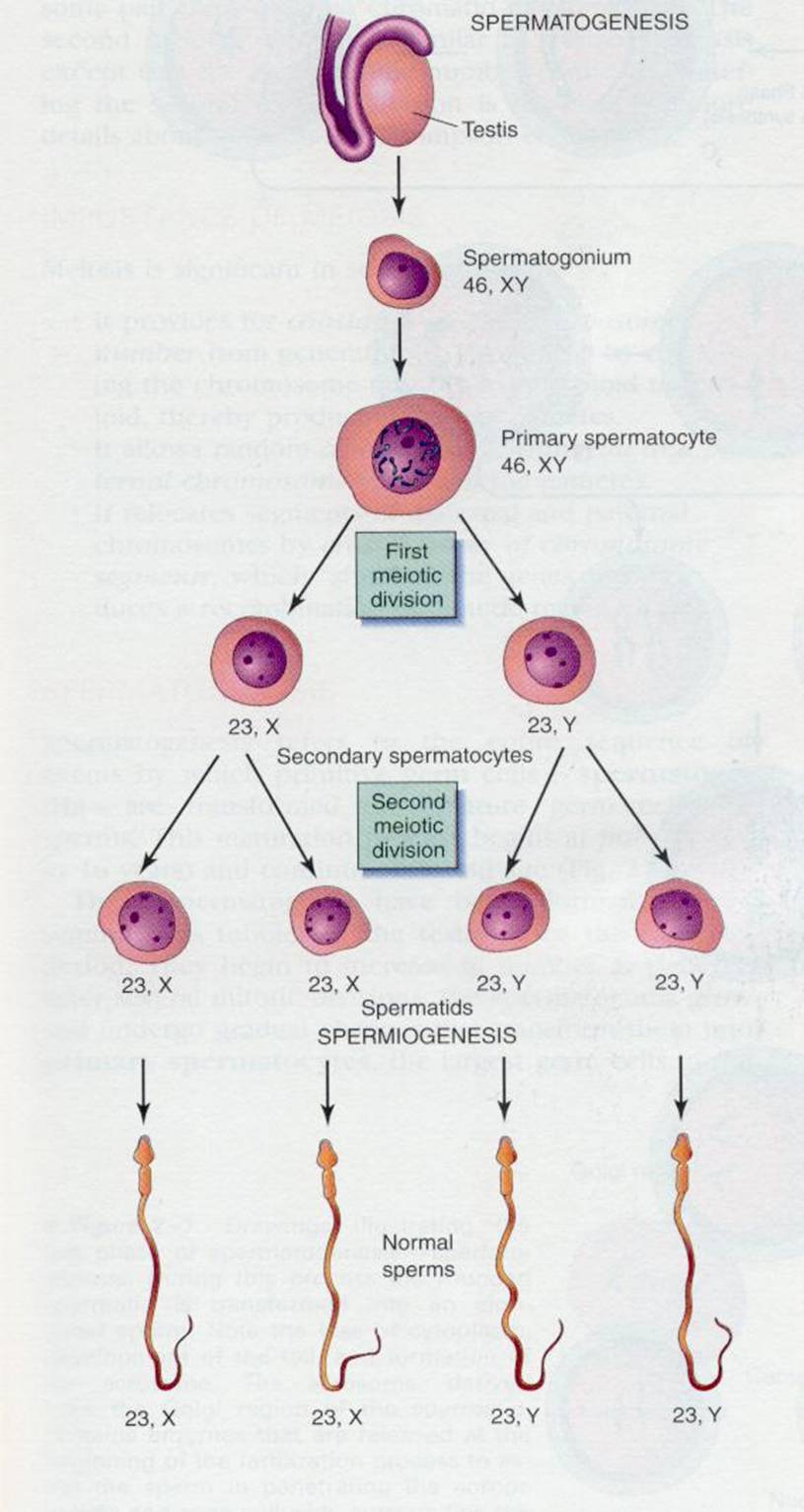
Spermiogeneis = details
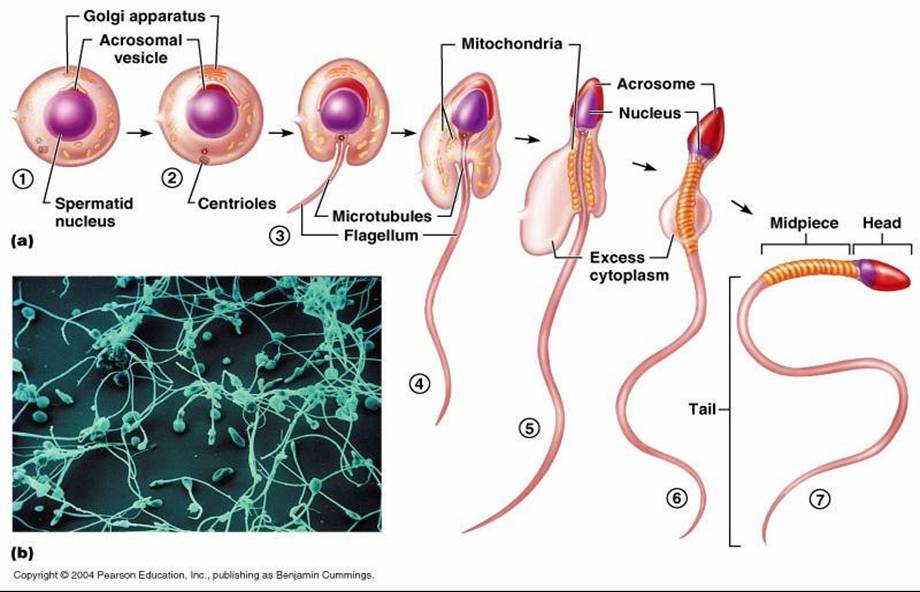

homunculus inside sperms

Sperm
using acrosome to disperse cumulus oophorus around egg
Components
of semen:
Seminal
Vesicle Fluid Components
•Fructose -
2º energy source for sperm
•Prostaglandin
– promotes contractions of the uterus & oviduct to help transport
sperm into ♀ tract
•Ascorbic acid
(vit. C) – anti-oxidant
•Ergothianine – activates sperm motility
•Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) – buffer to neutralize acidity of vagina
•Fibrinogen-like clotting proteins – clots semen
· Seminal vesicle fluid is responsible for the white
color of semen.
Prostatic
Fluid Components
•Zinc –
needed for fertility, keeps chromosomes tightly coiled. Zn makes up 60-70% of prostatic fluid.
•Sodium Citrate
– 1º source of energy, fuels mitochondria in sperm
•Acid phosphatase – activate sperm motility
•Polyamines
– activate sperm motility, inhibits bacterial growth, responsible for
distinctive odor of semen
•Enzymes
– activates the coagulation process of the clotting proteins
Cowper’s Gland Fluid
•Mucus to
–Rinse out urethra = neutralize urine
–May also add to lubrication during sex